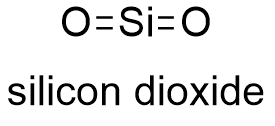|
CHEMICAL SUBSTANCE IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
Chemical name |
Silicon dioxide |
|
Synonyms |
Silica, Quartz, Silicic oxide, Silicon(IV) oxide, Crystalline silica, silica gel precipitated, crystalline-free* |
|
IUPAC name |
Silicon dioxide |
|
CAS No |
7631-86-9, 112926-00-8* |
|
REACH registration number |
|
|
EC No |
231-545-4 |
|
Molecular formula |
O2Si |
|
Substance group/chemical family |
mono-constituent substance/inorganic |
|
Appearance Physical state Odour Form Colour |
powder odourless crystalline and non-crystalline white |
|
USES AND HANDLING ISSUES |
|
|
Relevant identified uses |
It is used as filler in rubber products, paints, animal feeds, pedticides, insulation materials, and cosmetics. Silica nanoparticle applications include lukema cell biomarkers, cancer therapy, drug delivery, mechanical polishing, and additives to drugs, cosmetics, printing inks, varnishes, and food. Polycrystalline silicon and silicon dioxide materials are etched in semiconductor manufacturing. [3] |
|
Handling considerations |
Use safety glasses, lab coat, dust respirator, gloves. |
|
PHYSICO-CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
Molecular weight |
60,08 g/mol |
|
Bulk density/Specific gravity |
0,03-1 g/cm3 (20 °C) [5] /2,2 [8] |
|
pH |
3,5-9 (25 °C and 40-50 g/l) [5] |
|
EC |
|
|
Melting point |
1713 °C [5] |
|
Boiling point |
2950 °C |
|
Flash point |
|
|
Flammability |
|
|
Vapour density |
|
|
Vapour pressure |
13,3 hPa (1732 °C) [7] |
|
Solubility in water |
15-439,52 mg/l (20-37 °C, pH=5,5-7,4) [5] |
|
Solubility in organic solvents |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
|
|
Ionicity in water |
ion exchange processes possible [7] |
|
Surface tension |
|
|
Dispersion properties |
|
|
Specific surface (BET) |
50 to 400 m2/g (Synthetic amorphous silica, pyrogenic) [5] |
|
Stability and reactivity |
|
|
Chemical stability |
high stability [6] |
|
Reactivity hazards |
|
|
Corrosivity |
|
|
Polimerization |
|
|
Incompatibility with various substances |
|
|
Special remarks on reactivity |
|
|
Physical, chemical and biological coefficients |
|
|
Koc |
21.73 (The log of the adsorption coefficient (KOC) of Silica was estimated to be log KOC = 1.3370 which is equal to a KOC value of 21.73 using the KOCWIN v2.00 QSAR method) [5] |
|
Kow(log Pow) |
0.53 (25 °C, pH: 7) (QSAR method) [5] |
|
pKa |
|
|
Henry-constant |
9.652E-012 atm-m3/mole (9.780E-007 Pa-m3/mole)(at 25 °C) (QSAR method) [5] |
|
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE AND BEHAVIOUR |
|
|
Artificial pollution sources |
|
|
General terrestrial fate |
|
|
General aquatic fate |
|
|
General atmospheric fate |
|
|
General persistence and degradability |
|
|
Abiotic degradation and metabolites |
|
|
Biodegradation and metabolites |
not applicable [6] |
|
Bioconcentration |
not bioaccumulating due to inherent substance properties [7] |
|
Volatilization |
|
|
Photolysis |
stable |
|
Hydrolysis |
stable The level of maximum solubility: 2.7 mmol SiO2/litre, constant in a broad range of pH (1.1 < pH < 8.9). The surface of silica may be covered by a partial hydrolysed gel layer when in contact with water. [5] |
|
Soil adsorption and mobility |
The log of the adsorption coefficient (KOC) of Silica was estimated to be log KOC = 1.3370 which is equal to a KOC value of 21.73 using the KOCWIN v2.00 QSAR method. |
|
ENVIRONMENTAL CONCENTRATIONS |
|
|
Measured data |
|
|
ECOTOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION |
|
General adverse effects on ecosystem
|
|
|
Acute toxicity (LC50, EC50) |
|
|
Aquatic invertebrates
Aquatic algae and cyanobacteria
Sediment toxicity Terrestrial systems |
LC50 (4 days) 2.594 g/L [5] LC50 (48 h) 512.078 mg/L [5] EL50 (24 h) 1 g/L [5] EL0 (24 h) 1 g/L [5]
EC50 (4 days) 217.576 mg/L [5] EL50 (72 h) 10 g/L [5]
LC50 (14 days) 148.41 mg/kg sediment dw [5] |
|
Chronic toxicity (NOEC, LOEC) |
|
|
Aquatic invertebrates
Aquatic algae and cyanobacteria
Terrestrial systems |
NOEC (30 days) 34.223 - 346.737 mg/L [5]
NOEC (30 days) 42.11 mg/L [5] NOELR (72 h) 10 g/L [5] |
|
HUMAN HEALTH EFFECTS and PROTECTION |
|
|
Routes of human exposures |
oral, dermal, inhalation |
|
General effects |
Silicosis (i.e., nodular pulmonary fibrosis) caused by the inhalation and deposition of respirable crystalline silica particles [4] Pulmonary tuberculosis and other infections [4]
Lung cancer[4]
Autoimmune-related disease[4]
Renal disease[4]
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[4] |
|
Endocrine disruption |
|
|
Mutagenicity |
male rat alveolar cells, in vivo, inhalation, 3 mg/m3 aerosol (crystalline silica) 6hr/day, 5day/week for 13 week, positive [1 |
|
Carcinogenicity |
male, female rat – inhalation: 0; 50 mg/m3 6 hr/day, 5 day/week for up to 24 month (study duration 24month), lung: carcinoma or aenoma female rat – inhalation: 0; 1 mg/m3 6hr/day, 5day/week 24 month (study duration: 25,5 month), lung: tumor female rat – intratracheal: 3 mg of 0,09-0,2 μm particles given as 10 instillations before week 26, study duration 112 week or no treatment lung: Bronchiolo-alveolar adenoma (22/7 experimental animals vs 0/46 control animals), low incidence of begign tumors [1] |
|
Reprotoxicity |
|
|
Teratogenicity |
|
|
Skin, eye and respiratory irritations
Metabolism: absorption, distribution & excretion |
It is not irritating to skin and eyes. [6]
SAS forms [CAS No 7631-86-9] are rapidly eliminated from the lung tissue during and after prolonged inhalation exposure of experimental animals with no disproportionate disposition occurring in the mediastinal lymph nodes, whereas crystalline forms exhibit a marked tendency to accumulate and persist in the lung and lymph nodes. Intestinal absorption of SAS appears to be insignificant in animals and humans. There is evidence of ready renal elimination of bioavailable fractions. [6] |
|
Exposure limits |
NIOSH REL: TWA 6 mg/m3 [8] IDHL: 3000 mg/m3 [8] OSHA PEL: TWA 20 mppcf (80 mg/m3/ %SiO2) |
|
Drinking water MAC |
|
|
Other information |
fibrogenic [3] |
|
Animal toxicity data |
|
|
Acute toxicity (LD50) |
oral: LD50 5 000 mg/kg bw (rat) [5]
inhalation: LC50 (4 h) 140 - 58 800 mg/m³ air (rat) [5]
dermal: LD50 2 000 - 5 000 mg/kg bw (rabbit) [5]
|
|
Chronic toxicity (NOEL, LOEL) |
oral: NOAEL (rat): 2 500 mg/kg bw/day [5] NOEL (rat): 4 000 - 8 980 mg/kg bw/day [5] inhalation: NOAEC (rat): 1.3 - 10 mg/m³ air [5] NOEC (rat): 1.3 mg/m³ air [5] LOAEC (rat): 5.9 mg/m³ air [5] |
|
ENVIRONMENTAL STANDARDS AND REGULATIONS |
|
|
EINECS regulation |
|
|
OSHA regulations etc. |
|
|
OTHER INFORMATION, SPECIAL REMARKS |
|
|
CREATED, LAST UPDATE |
|
|
Created: Last update: |
10th April, 2018 29th May, 2018 |
|
REFERENCES |
|
|
[1] TOXNET – Toxicology Data Network. https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search2/f?./temp/~7yHgsY:4 [2] TOXNET – Toxicology Data Network. https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/7631-86-9 [3] Haz-Map. https://hazmap.nlm.nih.gov/category-details?table=copytblagents&id=620 [4] Chemical Safety Information from Intergovernmental Organizations. http://www.inchem.org/documents/cicads/cicads/cicad24.htm [5] European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). https://echa.europa.eu/brief-profile/-/briefprofile/100.028.678 https://echa.europa.eu/hu/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/15556 [6] OECD Existing Chemicals Database. https://hpvchemicals.oecd.org/UI/handler.axd?id=49b7307e-56d7-44d5-a15c-4e6d1ed25359 [7] OECD Existing Chemicals Database. https://hpvchemicals.oecd.org/UI/handler.axd?id=81d3694a-a582-4fa8-a8f2-f771459b67ed [8] OSHA – Occupal Safety and Health Administration, Occupational Chemical Database. https://www.osha.gov/chemicaldata/chemResult.html?recNo=613
|
|